What are Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a common health issue, affecting millions of people each year. These infections can occur in any part of the urinary tract, including the bladder, kidneys, ureters, and urethra. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for UTIs is crucial for maintaining urinary tract health.
What is a UTI?
A UTI is an infection caused by harmful bacteria that enter the urinary tract. These bacteria can multiply and cause inflammation, leading to uncomfortable symptoms and potential complications if left untreated.
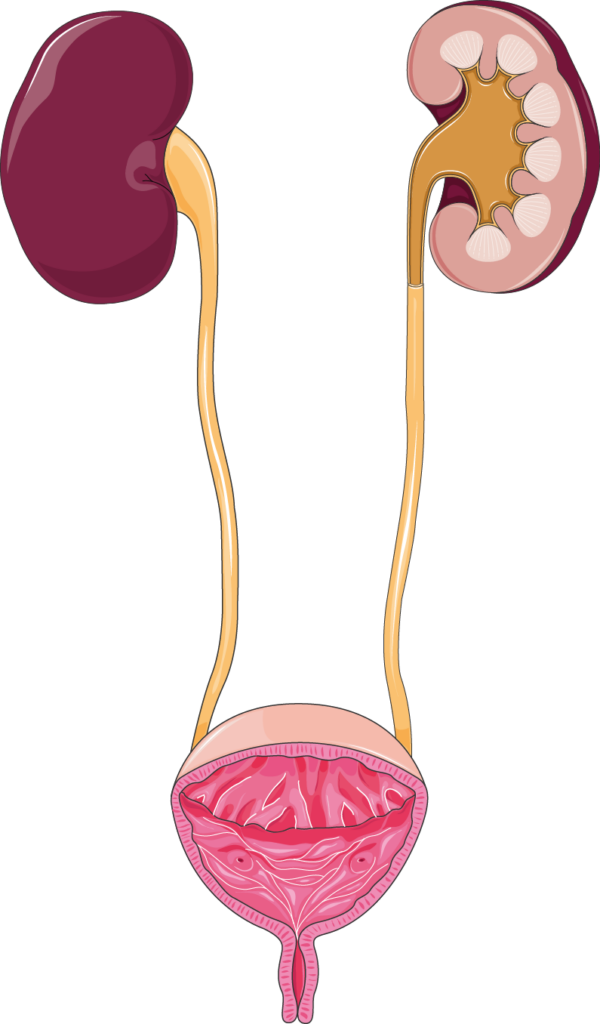
UTI by Sites
Infection can affect one or more parts of the urinary systems. The signs, symptoms and risk factors will vary depending on the specific organ involved. The four sites that constitute the urinary system are
- Kidneys – Pyelonephritis
- Ureters – Ureteritis
- Bladder -Cystitis
- Urethra – Urethritis
Causes of UTIs
The most common cause of UTIs is the bacteria Escherichia coli (E. coli), which is normally found in the gastrointestinal tract. Other bacteria, such as Klebsiella, Proteus, and Enterococcus, can also cause UTIs. Factors that increase the risk of developing a UTI include:
- Anatomical differences in the urinary tract
- Sexual activity
- Pregnancy
- Menopause
- Diabetes
- Urinary tract abnormalities or blockages
- Weakened immune system
- Poor hygiene
Symptoms of UTIs
The symptoms of a UTI can vary depending on the location and severity of the infection. Common symptoms include:
- Burning sensation or pain during urination
- Frequent or urgent need to urinate
- Cloudy, bloody, or foul-smelling urine
- Pelvic pain (in women)
- Rectal pain (in men)
- Fever and chills (in cases of a kidney infection)
Diagnosing UTIs
To diagnose a UTI, your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms, and perform a physical exam. Laboratory testing is essential in arriving at hte correct diagnosis. Cooomn tests for UTIs include:-
- Urine Analysis [urinalysis] to check for the presence of bacteria and white blood cells, which indicate an infection.
- Urine culture may be ordered to identify the specific type of bacteria causing the infection and determine the most effective antibiotic treatment.
- Complete blood count – To access the systemic manifestation of UTI. Elevated white blood cells are occasionally encountered.
- Kidney Function Tests [Urea, Electrolytes, Creatinine] especially where renal compromise is suspected
- C-reactive protein [CRP] – markers of inflammation may be necessary, especially in neonates in whom presentation of UTI may be unusual and making timely diagnosis is critical.
Treatment of UTIs
UTIs are typically treated with antibiotics, which help eliminate the harmful bacteria causing the infection. The specific antibiotic and duration of treatment will depend on the severity of the infection and the individual’s health status. In addition to antibiotics, other treatments may include:
- Pain relievers to alleviate discomfort
- Increased fluid intake to promote urination and flush out bacteria
- Avoidance of irritating hygiene products
- Probiotics to restore the balance of good bacteria in the urinary tract
Prevention of UTIs
To reduce the risk of developing a UTI, it is important to practice good hygiene and maintain a healthy lifestyle. Some preventive measures include:
- Drinking plenty of water to stay hydrated
- Urinating before and after sexual activity
- Wiping from front to back after using the bathroom
- Avoiding irritating hygiene products
- Wearing loose, breathable clothing
- Maintaining good genital hygiene
Complications Of UTI
Untreated UTIs can lead to serious complications. Urinary tract obstruction and stricture formation can constitute a medical emergency. Ascending infection can reach the kidneys, causing pyelonephritis and compromising kidney function.
Infection can spread to adjacent organs or systemically, leading to sepsis and shock. This is why UTIs are extremely dangerous in newborns and pregnant women
Conclusion: UTI Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment
In conclusion, UTIs are a common health issue that can be effectively treated with antibiotics and managed through preventive measures. If you suspect you have a UTI, it is important to seek medical attention promptly to prevent the infection from worsening or recurring.
Disclaimer
The information provided on this medical blog is for general informational purposes only and should not be considered as a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider before making any healthcare decisions or taking any actions based on the information provided on this blog. The authors and publishers of this blog are not liable for any errors or omissions in the content or for any actions taken based on the information provided.
