What is FNA?
Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA) is a minimally invasive diagnostic procedure used to obtain liquid tissue samples from various parts of the body for further examination. It is a valuable tool in diagnostic medicine, offering an affordable, reliable, and relatively simple method for obtaining diagnostic information. This article explores the key aspects of fine needle aspiration, including its indications, procedure, results, and the need for follow-up testing.
Uses of Fine Needle Aspiration in disease diagnosis
Fine Needle Aspiration is commonly used for the following purposes:
- Evaluation of palpable masses: FNA is an effective technique for investigating suspicious lumps or masses in different body regions, including the breast, thyroid, lymph nodes, and superficial soft tissues. It aids in the identification of potential malignancies or benign conditions.
- Characterization of cystic lesions: FNA can determine whether a cystic lesion contains fluid or solid components, helping to differentiate between benign and malignant growths.
- Diagnosis of deep-seated lesions: FNA is an alternative to more invasive procedures for obtaining tissue samples from organs such as the liver, kidney, and lung. It enables the evaluation of lesions that are not easily accessible or require more extensive surgeries.
FNA Procedure
The Fine Needle Aspiration procedure involves using a thin needle attached to a syringe to extract cells or fluid from the target site. The needle is guided into the suspicious area under palpation for superficial lesions or imaging guidance, such as ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), or fluoroscopy. Once the needle is accurately positioned, suction is applied to obtain the desired sample.
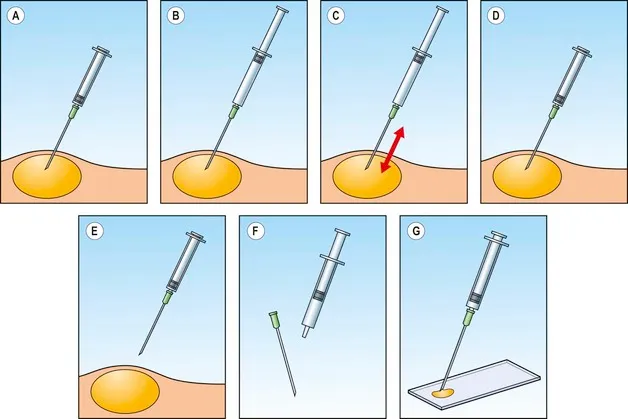
Type of Sample derived from FNA:
The samples obtained through Fine Needle Aspiration may vary depending on the target organ. It can involve aspirating cells, solid tissue fragments, or fluid from cystic lesions. The samples are collected in the syringe and prepared for further analysis.
How to Prepare for the FNA Procedure
Before undergoing Fine Needle Aspiration, patients may receive instructions such as:
- Informing healthcare providers about any medications, allergies, or bleeding disorders.
- Avoiding blood-thinning medications or herbal supplements that can increase the risk of bleeding.
- Fasting, if required, for specific procedures involving abdominal organs.
FNA is typically done as an outpatient procedure. Usually takes about 10 minutes. After the procedure, you may be given a paracetamol in case of pain.
Test Procedure:
The Fine Needle Aspiration procedure typically follows these steps:
- Patient positioning: The patient is positioned appropriately to provide access to the target area, ensuring comfort and safety during the procedure.
- Local anesthesia: Local anesthesia is administered to minimize discomfort during the needle insertion.
- Needle insertion: The healthcare provider uses imaging guidance to accurately position the needle into the target area. Once in place, the needle is moved back and forth to obtain the necessary samples.
- Sample collection: Aspiration is performed by applying gentle suction to the syringe attached to the needle, capturing the desired tissue or fluid sample.
- Needle removal and site care: After sample collection, the needle is removed, and pressure is applied to the puncture site to prevent bleeding. In some cases, a bandage or sterile dressing may be applied.
Sample processing:
After removal of an FNA sample, It usually either spreads on a microscope slide or an appropriate fixative is applied. For fluid samples, they are usually delivered to the lab for further processing eg cell block preparation. The prepared slides are stained with a dye to allow visualization of cells under a light microscope. Other tests like flow cytometry, immunocytochemistry/Immunohistochemistry, and molecular studies may be carried out as required.
Quality management is important at all times to ensure accurate results of FNA.
Results Interpretation:
Once the processing is completed, the pathologist or cytologist examines the slides under a microscope. The interpretation of the FNA depends on the target organ and the suspected condition. The pathologist will assess the sample for cellular abnormalities, infection, inflammation, or any other relevant findings. The results provide crucial information for the diagnosis and subsequent management plan.
Follow-up Testing:
In some cases, FNA may not provide a definitive diagnosis, and additional testing may be required. Follow-up testing can include further imaging studies, blood tests, or repeat biopsies to gather more information and confirm the diagnosis. The healthcare provider will determine the appropriate course of action based on the initial findings and clinical suspicion.
Cost of FNA procedure in Kenya
Several components such as the type of procedure, site or organ, and the nature if tests carried out afterwards determine the cost of FNA. The cost may vary from KES 1800 to as much as KES 40,000, depending on the above factors and the facility where its done. With prior authorization, health insurance and NHIF can cover the cost of FNA.
At our priority partner, Pathosure Diagnostic Center, Hurligham, you can get you FNA procedure and test results in 3 days.
Conclusion:
Fine Needle Aspiration is a valuable diagnostic tool that enables healthcare providers to obtain tissue samples with minimal invasiveness. It serves as an essential step in the diagnostic process, helping to determine the nature of suspicious masses, cystic lesions, and deep-seated abnormalities. With accurate guidance and interpretation of results, Fine Needle Aspiration contributes significantly to the early detection and management of various diseases, improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Hope this article helps you understand the basics of lipid profile test. Incase of any questions don’t hesitate to contact us or comment below.
If you found this helpful, help us reach out to more people by liking and sharing with friends and family. Consider subscribing to our blog so we alert you when we publish new articles.
Till next time, happy and healthy living!
Team labtestzote.
Disclaimer
The information provided on this medical blog is for general informational purposes only and should not be considered as a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider before making any healthcare decisions or taking any actions based on the information provided on this blog. The authors and publishers of this blog are not liable for any errors or omissions in the content or for any actions taken based on the information provided.
Medically reviewed by:
Dr Mwaura J
