What is testicular Cancer?
Testicular cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the testicles, which are part of the male reproductive system. It is the most common cancer in young men aged 15 to 35 years. Testicular cancer usually starts in the germ cells, which are the cells that make sperm[1][3].
Summary /Key Points about Testicular Cancer
- Testicular cancer is highly treatable and curable, especially when detected early.
- The most common symptom is a painless lump or swelling in the testicle.
- Risk factors include undescended testicle, family history, and personal history of testicular cancer.
- Treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy
Read More ▶▶▶Key Facts about Cancer in Kenya
Prevalence and Incidence of Testicular Cancer in Kenya
Testicular cancer is rare, affecting only about 1 in 250 people with testicles in their lifetimes. It is estimated that more than 1,000 people were diagnosed with testicular cancer in Australia in 2023, and the average age at diagnosis is 36 years old.6
Risk Factors
Risk factors for testicular cancer include[3][4]:
- Undescended testicle (cryptorchidism)
- Family history of testicular cancer
- Personal history of testicular cancer
- Infertility
- HIV and AIDS
- Hypospadias (a birth defect where the urethra opens on the underside of the penis)
- Regular cannabis use
Signs and Symptoms
The most common symptom of testicular cancer is a painless lump or swelling in the testicle.
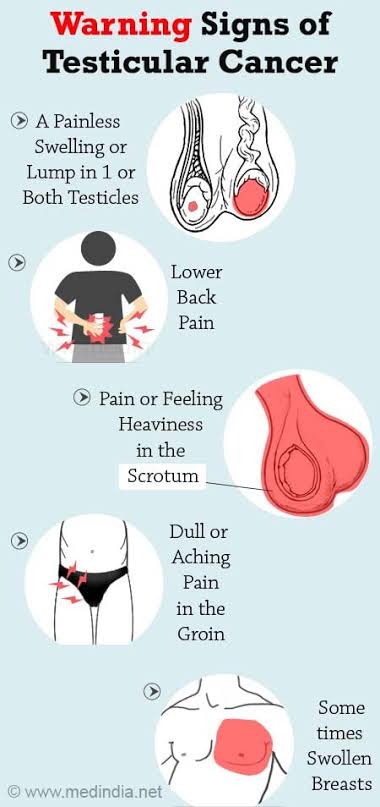
Other symptoms may include:-
- Feeling of heaviness in the scrotum
- Feeling of unevenness
- Pain or ache in the lower abdomen, the testicle, or scrotum
- Back pain
- Enlargement or tenderness of the breast tissue (due to hormones created by cancer cells)
Reducing Your Risk of Testicular Cancer
There are no known prevention strategies for testicular cancer. However, regular self-examination of the testicles can help detect any changes or abnormalities early.
Screening and Early Diagnosis
Screening for testicular cancer typically involves 2 approaches
- Physical exam by a healthcare provider
- Ultrasound of the testicles
- Blood tests for tumor markers
Diagnosis of Testicular Cancer
The only way to definitively diagnose testicular cancer is through surgical removal of the affected testicle (orchiectomy). This is because cutting into a testicle could potentially spread the cancer to other parts of the body.
Related: Threat of Prostate Cancer in Kenya
How is Testicular Cancer Treated?
Treatment for testicular cancer depends on the stage of the cancer and may include the following:-
- Surgery (orchiectomy)
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- High-dose chemotherapy with stem cell transplant
- Surveillance (close monitoring with regular exams and tests)
The prognosis for testicular cancer is excellent, with a cure rate of over 95% when treated early[3]. Even in advanced cases, the cure rate is around 50%[3].
References
- What is Testicular Cancer? [cancer.org]
- Testicular Cancer [Medlineplus]
- Brief Overview Of Testicular Cancer [Cleveland Clinic]
- Symptoms of Testicular Cancer [Mayo Clinic]
Related Tests In this Post
-
Alpha Fetal Protein AFP TestKSh3,150
Disclaimer
The information provided on this medical blog is for general informational purposes only and should not be considered as a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider before making any healthcare decisions or taking any actions based on the information provided on this blog. The authors and publishers of this blog are not liable for any errors or omissions in the content or for any actions taken based on the information provided.
