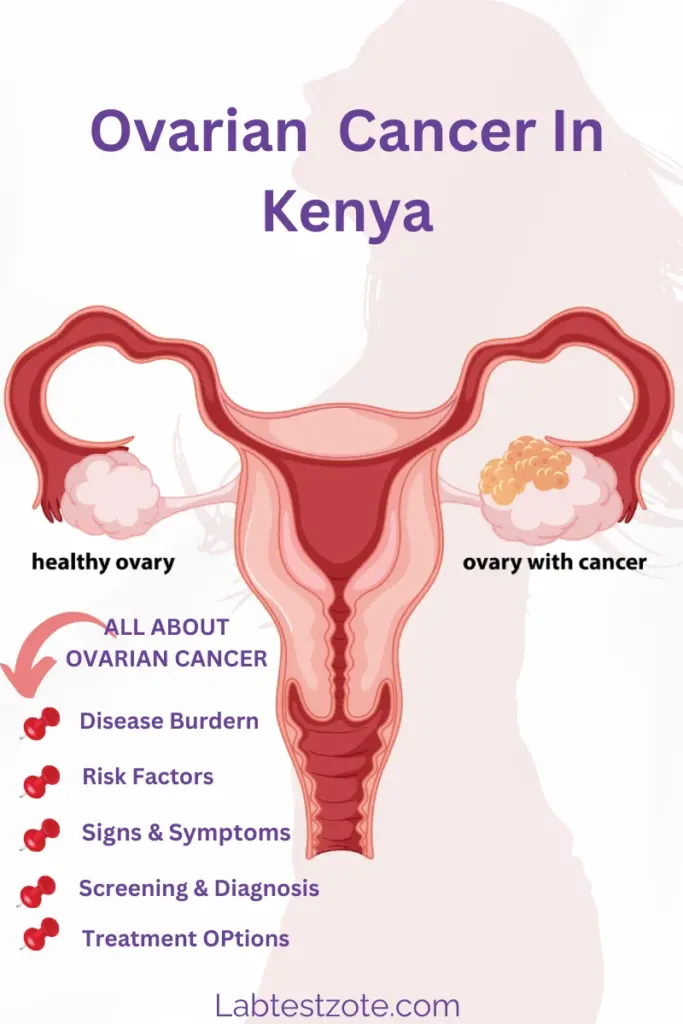
What is Ovarian Cancer?
Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the ovaries, the female reproductive organs responsible for producing eggs and the female hormones estrogen and progesterone. It is a serious and often deadly disease, but with early detection and proper treatment, many women can be cured. In this blog post, we will explore the key aspects of ovarian cancer, focusing on the Kenyan context.
Table of Contents
- What is Ovarian Cancer?
- Key Points/Summary
- Why Ovarian Cancer is an Important Public Health Conern
- Risk Factors for Ovarian Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer Signs and Symptoms
- Keeping Ovarian Cancer at Bay :Prevention Strategies
- How to Screen for Ovarian Cancer
- Diagnosis Of Ovarian Cancer
- Treatment and Management
- Tests Mentioned In this Post
- Sharing is Caring
- Author
Key Points/Summary
- Ovarian cancer is a serious and often deadly disease that begins in the ovaries.
- Early detection is crucial for successful treatment, but symptoms are often vague and difficult to recognize.
- Risk factors include age, family history, and certain genetic mutations.
- Prevention strategies include oral contraceptives and prophylactic surgery for high-risk women.
- Screening, diagnosis, and treatment require specialized care from gynecologic oncologists.
Why Ovarian Cancer is an Important Public Health Conern
In Kenya, ovarian cancer is the second most common gynecologic cancer after cervical cancer. According to the National Cancer Registry, ovarian cancer accounts for approximately 4% of all cancer cases in the country. The incidence rate is estimated to be around 3.8 per 100,000 women per year.
Risk Factors for Ovarian Cancer
The main risk factors for ovarian cancer include:
- Age: The risk increases with age, with most cases occurring in women over 50.
- Family history: Women with a first-degree relative (mother, daughter, or sister) with ovarian cancer have a higher risk.
- Genetic mutations: Certain genetic mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, increase the risk of ovarian cancer.
- Infertility and fertility treatments: Women who have never been pregnant and those who have used fertility treatments may have a slightly higher risk.
Ovarian Cancer Signs and Symptoms
Early-stage ovarian cancer often has vague and non-specific symptoms, making it difficult to diagnose. The most common symptoms include:
- Abdominal bloating or discomfort
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Difficulty eating or feeling full quickly
- Urinary symptoms, such as urgency or frequency
If you experience any of these symptoms for more than a few weeks, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider.
Keeping Ovarian Cancer at Bay :Prevention Strategies
While there is no sure way to prevent ovarian cancer, there are some strategies that may help reduce the risk:
- Oral contraceptives: Using birth control pills for at least 3-6 months can reduce the risk of ovarian cancer by up to 50%.
- Prophylactic surgery: Women at high risk due to genetic mutations or family history may consider having their ovaries and fallopian tubes removed (prophylactic bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy) to reduce the risk of ovarian cancer.
How to Screen for Ovarian Cancer
Screening is a medical procedure that helps at detecting diseases at the earliest stage, before symptoms appear.
There is currently no effective screening test for ovarian cancer in the general population. However, women at high risk due to genetic mutations or family history may be offered:
- Transvaginal ultrasound: This imaging test can help detect abnormalities in the ovaries.
- CA-125 blood test: This test measures the levels of a protein called CA-125, which can be elevated in ovarian cancer.
Diagnosis Of Ovarian Cancer
If ovarian cancer is suspected, the following tests may be used for accurate and timely diagnosis:
- Pelvic exam: The doctor will feel the ovaries and surrounding organs for any abnormalities.
- Imaging tests: Transvaginal ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI may be used to get a better look at the ovaries and surrounding tissues.
- Biopsy: A small sample of tissue from the ovary may be removed and examined under a microscope to check for cancer cells.
Treatment and Management
Treatment for ovarian cancer depends on the stage of the disease, the type of cancer, and the woman’s overall health. The main treatment options include:
- Surgery: The goal of surgery is to remove as much of the visible tumor as possible. This may involve removing one or both ovaries, the fallopian tubes, the uterus, and nearby lymph nodes.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy drugs are used to kill cancer cells. It may be given before or after surgery, or as the main treatment for advanced-stage ovarian cancer.
- Targeted therapy: Newer drugs that target specific genetic changes in cancer cells may be used in some cases.
In conclusion, ovarian cancer is a serious disease, but with early detection and proper treatment, many women can be cured. If you experience any symptoms or have a family history of ovarian cancer, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider. Regular check-ups and screening for high-risk women can help detect the disease early and improve the chances of successful treatment.
Tests Mentioned In this Post
-
Histology for Biopsies and Surgical Specimens (Small Specimen)KSh4,750
-
CA-125 TestOriginal price was: KSh2,650.KSh2,350Current price is: KSh2,350.
-
BRCA-2 Gene Mutation TestOriginal price was: KSh134,025.KSh75,000Current price is: KSh75,000.
-
BRCA1-2 Gene Mutation AnalysisKSh65,000
-
Bone Marrow Examination (Aspiration & Trephene Biopsy)KSh14,950
Disclaimer
The information provided on this medical blog is for general informational purposes only and should not be considered as a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider before making any healthcare decisions or taking any actions based on the information provided on this blog. The authors and publishers of this blog are not liable for any errors or omissions in the content or for any actions taken based on the information provided.
