What is multiple myeloma?
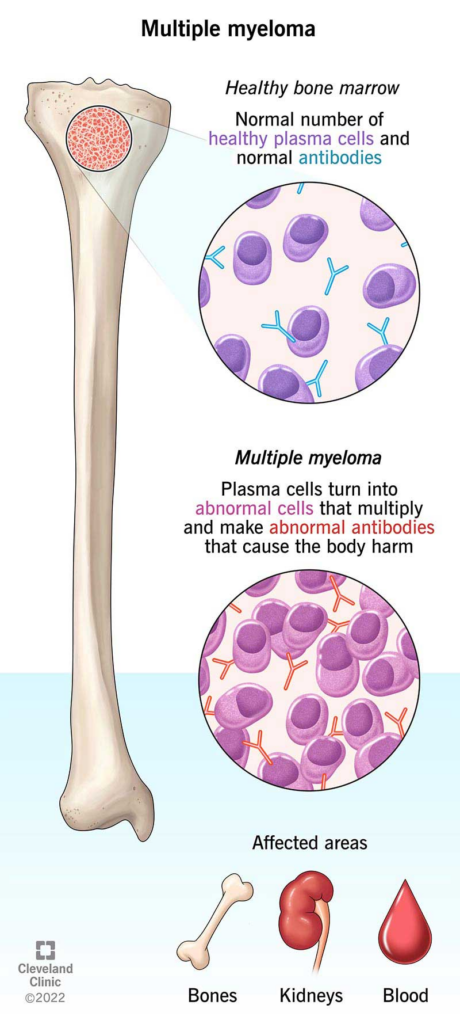
Multiple myeloma, also known as plasma cell myeloma, is a rare type of blood cancer that affects plasma cells in the bone marrow. These cancerous plasma cells produce abnormal antibodies, leading to various complications in the body.
Key Points/Summary
- Multiple myeloma is characterized by the abnormal growth of plasma cells in the bone marrow, crowding out healthy blood cells and producing dysfunctional proteins.
- It is a cancer that affects the immune system, bones, kidneys, and blood cell production.
- While there is no known cure for multiple myeloma, treatments aim to manage symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve quality of life.
- The disease is more common in older adults, with men being more affected than women.
- Risk factors include genetic mutations, age, family history, and certain chemicals.
Prevalence/Incidence
- Multiple myeloma is rare, affecting about 7 people out of 100,000 each year in the United States.
- Globally, around 175,000 people were diagnosed with the disease in 2020, with about 117,000 deaths reported.
Risk Factors
- Risk factors for multiple myeloma include obesity, radiation exposure, family history, age, and certain chemicals.
- There is an increased risk in certain occupations due to exposure to aromatic hydrocarbon solvents.
Signs and Symptoms
- Symptoms of multiple myeloma can include bone pain, fatigue, anemia, kidney problems, high calcium levels, infections, and weakened bones that are prone to fractures.
Prevention Strategies
- As the exact cause of multiple myeloma is unknown, prevention strategies focus on managing risk factors such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle and avoiding exposure to harmful chemicals.
Screening Modalities
- Diagnosis of multiple myeloma involves blood and urine tests, bone marrow biopsy, and medical imaging to detect abnormal plasma cells and bone lesions.
Diagnosis
- Multiple myeloma is diagnosed based on abnormal antibody proteins in blood or urine tests, cancerous plasma cells in bone marrow biopsy, and bone lesions in medical imaging.
Treatment and Management
- Treatment options for multiple myeloma include anti-myeloma medicines, chemotherapy, stem cell transplant, and supportive care to manage symptoms and complications.
- While most cases cannot be cured, treatments aim to control the disease and improve quality of life.
In conclusion, multiple myeloma is a complex blood cancer that requires ongoing management and care. Understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and available treatments is crucial for individuals affected by this condition. Stay informed, seek medical advice, and take proactive steps to manage multiple myeloma effectively.
Laboratory Tests Related to Multiple Myeloma
Disclaimer
The information provided on this medical blog is for general informational purposes only and should not be considered as a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider before making any healthcare decisions or taking any actions based on the information provided on this blog. The authors and publishers of this blog are not liable for any errors or omissions in the content or for any actions taken based on the information provided.
