Introduction
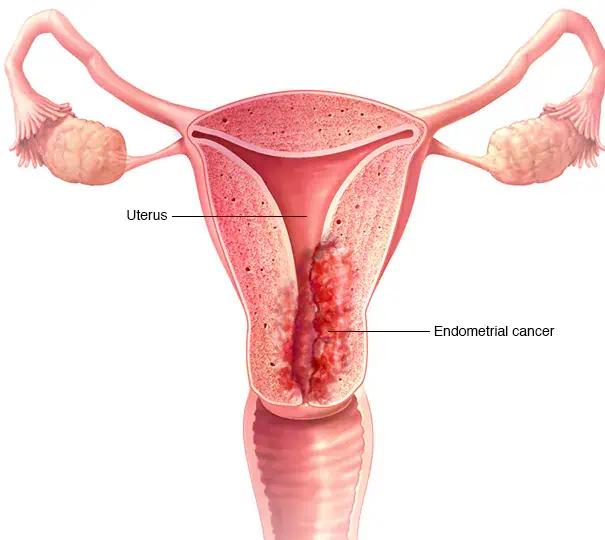
Endometrial cancer, also known as uterine cancer, originates in the endometrium, the lining of the uterus. It is the most common type of uterine cancer, affecting women primarily in their 60s and 70s. The exact cause is not fully understood, but factors like estrogen levels, obesity, and certain medical conditions can increase the risk.
Key Points/Summary
Endometrial cancer arises from abnormal cell growth in the uterus lining. Symptoms include abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, and postmenopausal bleeding. Early detection is crucial for successful treatment.
Prevalence/Incidence
Endometrial cancer accounts for a significant portion of new cancer cases, with around 66,200 new cases diagnosed annually in the United States.
Risk Factors
Risk factors include hormonal imbalances, obesity, late menopause, and never being pregnant. Hormone therapy and certain medications can also elevate the risk.
Signs and Symptoms
Symptoms of endometrial cancer encompass abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, and postmenopausal bleeding. Prompt medical attention is essential if these signs manifest.
Related: Cervical Cancer Screening in Kenya
Prevention Strategies
Maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, and managing hormone levels can help reduce the risk of endometrial cancer. Consultation with healthcare providers for personalized advice is crucial.
Screening Modalities
Screening for endometrial cancer involves tests like endometrial biopsy, pelvic exams, and ultrasounds. Early detection through screening can improve treatment outcomes.
Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer
Diagnosis of endometrial cancer involves various tests like endometrial sampling, Pap smears, and imaging studies to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
Endometrial Sampling Or Biopsy
An endometrial biopsy is the definitive method for diagnosing endometrial cancer. During this procedure, a thin tube is inserted through the cervix into the uterus to collect a sample of the endometrial tissue. This sample is then examined under a microscope for cancerous cells. The biopsy can often be performed in a healthcare provider’s office and is crucial for confirming the diagnosis
Treatment and Management
Treatment options for endometrial cancer include surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and hormonal therapy. The choice of treatment depends on the cancer stage and individual health factors.
Conclusion
Understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and screening methods for endometrial cancer is vital for early detection and effective management. Regular health check-ups and awareness of one’s body can contribute significantly to combating this prevalent form of cancer.
Disclaimer
The information provided on this medical blog is for general informational purposes only and should not be considered as a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider before making any healthcare decisions or taking any actions based on the information provided on this blog. The authors and publishers of this blog are not liable for any errors or omissions in the content or for any actions taken based on the information provided.