What is cancer and why is it a significant health issue in Kenya?
Cancer, a complex group of diseases, originates from abnormal cell growth that invades surrounding tissues and can spread to other parts of the body. It is a significant global health concern, ranking as the second leading cause of death worldwide. The impact of cancer extends beyond physical health, affecting emotional and financial well-being.
Key Points/Summary about cancer in Kenya
- Cancer arises from uncontrolled cell growth and can metastasize, leading to severe consequences.
- Prevention strategies, early detection, and timely treatment play crucial roles in combating cancer.
- Lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding tobacco, maintaining a healthy weight, and regular exercise, can reduce cancer risk.
- Genetic factors, virus exposure, and environmental influences contribute to cancer development.
Burden of Cancer in Kenya
Globally, cancer accounts for millions of deaths annually, with specific types more prevalent in men and women. The burden of cancer disproportionately affects low- and middle-income countries.
Here are the key stats about cancer in Kenya, according to Globocan, the National Cancer Registry and the Ministry of Health (year 2022)

30 commonest cancers in Kenya -Ranked
(Click on the type to learn more about it)
| Rank | Cancer | New Cases | (%) | No. Deaths | Rank | (%) | Number | Prop. (per 100 000) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Breast | 7 243 | 16.2 | 3 398 | 2 | 11.6 | 18 698 | 18.3 |
| 2 | Cervix | 5 845 | 13.1 | 3 591 | 1 | 12.2 | 14 974 | 14.7 |
| 3 | Prostate | 3 582 | 8.0 | 2 029 | 5 | 6.9 | 6 863 | 6.7 |
| 4 | Oesophagus | 3 340 | 7.5 | 3 132 | 3 | 10.7 | 5 129 | 5.0 |
| 5 | Colorectum | 3 091 | 6.9 | 2 116 | 4 | 7.2 | 7 326 | 7.2 |
| 6 | Stomach | 1 899 | 4.2 | 1 595 | 6 | 5.4 | 3 048 | 3.0 |
| 7 | Leukaemia | 1 729 | 3.9 | 1 252 | 7 | 4.3 | 4 396 | 4.3 |
| 8 | Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma | 1 680 | 3.8 | 1 089 | 8 | 3.7 | 4 544 | 4.4 |
| 9 | Ovary | 1 245 | 2.8 | 894 | 9 | 3.0 | 2 928 | 2.9 |
| 10 | Nasopharynx | 948 | 2.1 | 619 | 15 | 2.1 | 2 512 | 2.5 |
| 11 | Lung | 903 | 2.0 | 822 | 11 | 2.8 | 1 397 | 1.4 |
| 12 | Pancreas | 889 | 2.0 | 872 | 10 | 3.0 | 1 027 | 1.0 |
| 13 | Liver | 883 | 2.0 | 819 | 12 | 2.8 | 1 372 | 1.3 |
| 14 | Uterus | 829 | 1.9 | 257 | 21 | 0.88 | 2 347 | 2.3 |
| 15 | Multiple myeloma | 800 | 1.8 | 677 | 13 | 2.3 | 1 924 | 1.9 |
| 16 | Lip, oral cavity | 751 | 1.7 | 438 | 16 | 1.5 | 1 825 | 1.8 |
| 17 | Brain CNS | 736 | 1.6 | 634 | 14 | 2.2 | 2 225 | 2.2 |
| 18 | Kaposi sarcoma | 658 | 1.5 | 383 | 17 | 1.3 | 1 504 | 1.5 |
| 19 | Bladder | 547 | 1.2 | 272 | 20 | 0.93 | 1 348 | 1.3 |
| 20 | Kidney | 516 | 1.2 | 334 | 19 | 1.1 | 1 409 | 1.4 |
| 21 | Thyroid | 445 | 1.00 | 144 | 24 | 0.49 | 1 178 | 1.2 |
| 23 | Gallbladder | 428 | 0.96 | 366 | 18 | 1.2 | 683 | 0.67 |
| 24 | Hodgkin lymphoma | 422 | 0.94 | 182 | 23 | 0.62 | 1 270 | 1.2 |
| 25 | Larynx | 366 | 0.82 | 236 | 22 | 0.81 | 953 | 0.93 |
| 26 | Melanoma | 265 | 0.59 | 94 | 26 | 0.32 | 712 | 0.70 |
| 27 | Vulva | 163 | 0.36 | 82 | 28 | 0.28 | 421 | 0.41 |
| 28 | Salivary glands | 152 | 0.34 | 87 | 27 | 0.30 | 407 | 0.40 |
| 29 | Hypopharynx | 142 | 0.32 | 112 | 25 | 0.38 | 237 | 0.23 |
| 30 | Oropharynx | 87 | 0.20 | 55 | 29 | 0.19 | 190 | 0.19 |
| 31 | Vagina | 59 | 0.13 | 32 | 30 | 0.11 | 134 | 0.13 |
| 32 | Penis | 51 | 0.11 | 22 | 31 | 0.08 | 132 | 0.13 |
| 33 | Testis | 36 | 0.08 | 11 | 32 | 0.04 | 107 | 0.11 |
| All cancers | 44 726 | – | 29 317 | – | – | 102 152 | – | |
| All cancers excl. NMSC | 44 065 | – | 29 091 | – | – | 100 307 | – |
Risk Factors for Cancer
Cancer is a complex disease and its causation is determined by the interplay between many independent t or related factors.
Apart from a few cancers such as cervical cancer, It’s usually hard to designate any one factor as the definitive cause of cancer. Many to note no one causative agent is ever found. Key risk factors include :
💣Tobacco use
💣Unhealthy diet
💣Alcohol consumption
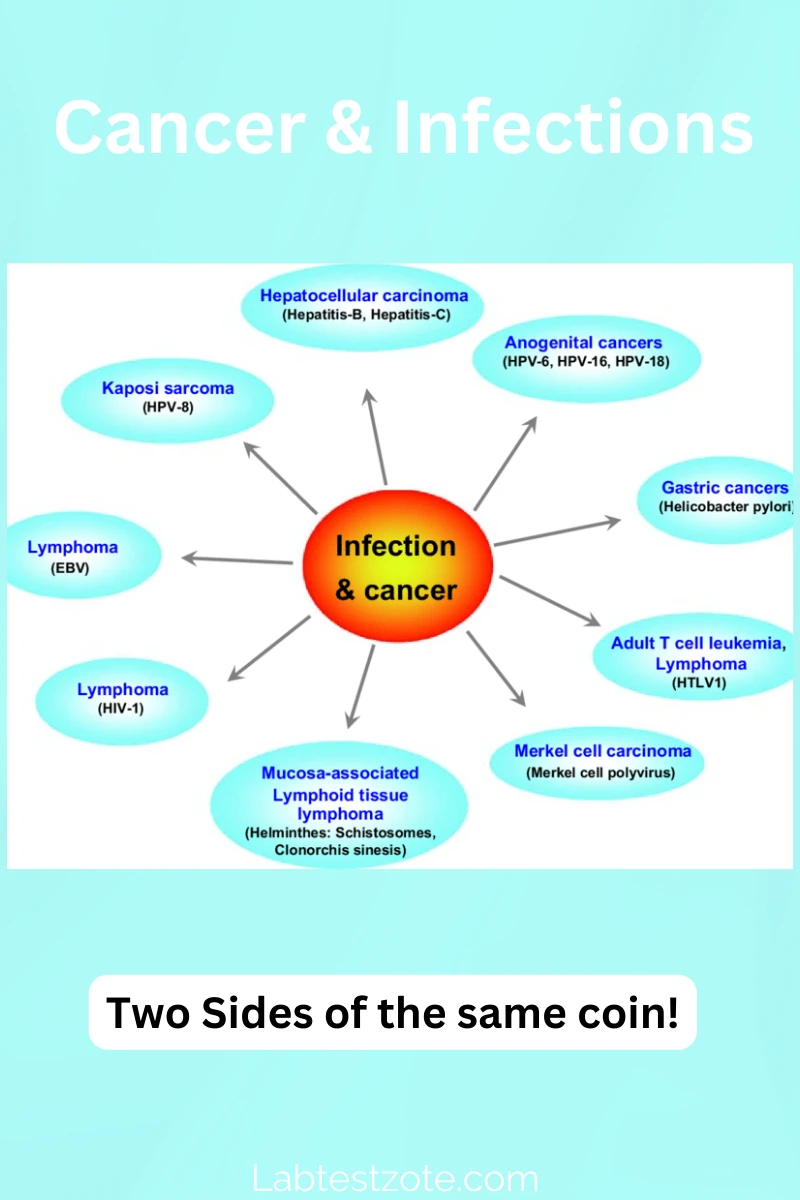
💣Infectious diseases including bacterial and viral infections
💣Genetic predisposition.
💣Environmental exposure
💣Lifestyle choices significantly impact cancer risk for example obesity
Signs and Symptoms of symptoms of cancer
Cancer symptoms vary depending on the type and location. Sometimes cancer may not cause any ill health or may mimic symptoms of other common diseases.
Some common symptoms include;-
🩺unexplained weight loss,
🩺persistent fatigue,
🩺lumps and swellings
🩺changes in bowel habits.
🩺Bleeding for example from genital areas, coughing blood, blood in stool or urine.
Early detection is crucial for effective treatment, so ensure regular screening.
Prevention Strategies for cancer in Kenya
Preventing cancer involves lifestyle changes, vaccination against specific viruses, and reducing exposure to carcinogens. Regular screenings and awareness of risk factors are essential for prevention.
1. Screening for cancer
Screening tests help detect cancer early before symptoms appear, improving treatment outcomes. Screening guidelines vary based on cancer type and individual risk factors.
2. Vaccinations
HPV vaccine is very effective in preventing cervical cancer
3. Early and effective Treatment for Infections
Schistosomiasis (bilharzia), H.pylori, HPV, HIV, EBV are common infections in kenya. These pathogens are implicated in casuation of varoius cancers. Early treatment can help reduce cacner burden related to these infections
4. Lifestyle and dietary changes
Maintaing a healthy, active lifestyle can help reduce your risk to cancer. Being intentional about diet and maintaining healthy weight can go a long way. For example, “Chama Choma”, a common delicay in Kenya has been shown to contain carcinogenic elements.
5. Avoiding envrironmental exposures
Some compunds such as pesticides, paint components,
Diagnosis of cancer in Kenya
Diagnosing cancer involves a combination of thoruogh history and physical examination, imaging tests, biopsies, and laboratory analyses to confirm the presence of cancer cells and determine the type and stage of cancer.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory plays a central role in screening, diagnosis and monitoring progress and response to treatment.
some of the tests usef are:-
- Baseline tests – help in evaluating overall health
- Tumor markers
- Specialised tests
- Biopsy – histology and cytology
- Molecular studies
Its imporant to note all these tests may be used in different combinations to help in diagnosis and folloup of cacner patient
Treatment and Management of cancer
Treatment options for cancer include
💉surgery,
💉chemotherapy,
☢radiation therapy,
🎯targeted therapy
💉immunotherapy
Multidisciplinary teams tailor treatment plans to individual patients, considering factors like cancer stage and patient preferences.
Read More: Posts You May Be interested In
Unholy Alliance – Dangerous Relationship Between Infectious Diseases And Cancer
How are Infectious Diseases And Cancer Related? The connection between infectious diseases and cancer is…
Understanding Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) – A Common Childhood Blood Cancer In Kenya
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a type of blood cancer that starts from young white…
Thyroid Cancer – What you need to know about Causes, Signs &Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment Options
I understand. Let’s create an engaging blog post on thyroid cancer with a focus on…
The Reality of Liver Cancer in Kenya: What You Need to Know to Stay Safe
Introduction to Lung Cancer Liver cancer, also termed Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a significant health…
Conclusion: Hope for cancer in Kenya
In conclusion, understanding cancer’s complexity, promoting prevention strategies, and advocating for early detection are vital in the fight against this challenging disease. Stay informed, prioritize your health, and seek medical advice for any concerning symptoms.
Citations:
[1] https://www.who.int/health-topics/cancer
[2] https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2311300617300125
[3] https://www.uhhospitals.org/health-information/health-and-wellness-library/article/Adult-Diseases-and-Conditions-v0/cancer-overview
[4] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29952494/
[5] https://www.medicinenet.com/cancer/article.htm
Disclaimer
The information provided on this medical blog is for general informational purposes only and should not be considered as a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider before making any healthcare decisions or taking any actions based on the information provided on this blog. The authors and publishers of this blog are not liable for any errors or omissions in the content or for any actions taken based on the information provided.